Nanofibers have unique properties that distinguish them from other one-dimensional structures such as nanowires and nanorods. Nanofiber structures are produced in composite, ceramic, and especially polymeric materials with diverse morphologies. When polymer fibers are reduced from several micrometers to below 100 nm, amazing properties such as a very high surface-to-volume ratio (this ratio is 1000 times larger for nanofibers than microfibers), very low density due to very high porosity and controllability And the flexibility of surface properties and excellent mechanical performance such as hardness and high tensile strength appear in these materials.
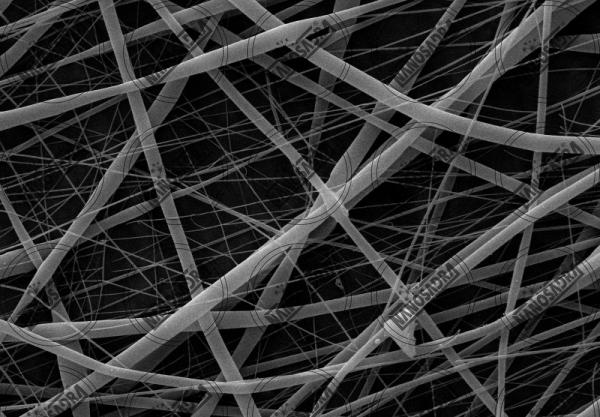

What are electrospun nanofibers?
 The electrospinning process is a simple and widely used method for the production of polymer, ceramic, and composite nanofibers. Today, the electrospinning process has been extended to produce nanofibers with various structures such as hollow, core-shell and porous structures. These structures have received considerable attention because of their surface-to-volume ratio and their length-to-diameter ratio and have high potential for use in various applications. In this paper, the properties and applications of nanofibers produced by electrospinning are investigated. Nanofibers have a variety of applications including defense, tissue engineering, filtration, sensors, cosmetics and more. For more information you can search these words on the internet:
The electrospinning process is a simple and widely used method for the production of polymer, ceramic, and composite nanofibers. Today, the electrospinning process has been extended to produce nanofibers with various structures such as hollow, core-shell and porous structures. These structures have received considerable attention because of their surface-to-volume ratio and their length-to-diameter ratio and have high potential for use in various applications. In this paper, the properties and applications of nanofibers produced by electrospinning are investigated. Nanofibers have a variety of applications including defense, tissue engineering, filtration, sensors, cosmetics and more. For more information you can search these words on the internet:
- nanofiber solutions
- nanofibers introduction
- advantages of nanofibers
Since the electrospinning process is accompanied by rapid jet stretching under the electric field and solvent evaporation, so much shear force is applied to the polymer chain during the electrospinning process. This shear force results in the regular alignment of a part of the polymer chains and their parallel alignment. The rapid freezing of the polymer jet prevents the regular chains from returning to their original equilibrium state. The formation of regular regions in different parts of nanofibers will increase the crystallinity of nanofibers. Increasing the crystallinity of polymer nanofibers during the electrospinning process has a significant effect on the other physical and mechanical properties of the scaffold.
What are nanofibers made of?
In general, one-dimensional hollow nanostructures (such as nanotubes) are of great importance in various domains such as electronics, nanofluids, energy storage, microcapsules for controlled drug release, catalysts and sensors. In recent years, a variety of methods have been developed for the production of polymer nanofibers, including synthetic methods using preconfigured patterns, phase separation, self-assembly and electrospinning.
In the meantime, the electrospinning process is one of the simplest and most versatile ways to produce a variety of nanofibers, such as hollow, core-shell, and porous nanofibers with uniform diameters. This method, in addition to providing electrostatic repulsion between surface charges (rather than shear or mechanical forces) for continuous reduction of viscoelastic jet diameter, is similar to other aspects of commercial microfibre production by mechanical spinning.
Compared to mechanical spinning, electrostatic or electrostatic spinning has the ability to produce smaller diameter fibers. Electrification is a continuous process and can be used for mass production of everyday and industrial products.
The electrospinning process is very similar to the electrostatic or electrospray spraying process. In both of these methods, high voltage is used to form a liquid jet. In the electrospray process, very small particles are sprayed on a substrate surface during a continuous flow of soluble jet (often low viscosity). In the electrospinning process, solid fibers are produced by evaporating the solvent in a continuous jet of the desired solution. This continuous jet is composed of electrostatic forces caused by surface electric charges.
Distributors and wholesalers of nanofibers in Asia
 At present, with the use of all-electromagnetic equipment, the production of nanofibers from more than 5 polymer and ceramic materials has been successful in Asian technology companies. The polymers used comprise a variety of synthetic or natural biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers. It should be noted that Asian technology companies with more than five years of scientific and practical experience in the field of electronics processes have a variety of potential nanotechnology products that can be applied to a variety of nanofiber products for use in the medical and industrial fields. Isolation and filtration systems are noted.
At present, with the use of all-electromagnetic equipment, the production of nanofibers from more than 5 polymer and ceramic materials has been successful in Asian technology companies. The polymers used comprise a variety of synthetic or natural biodegradable and non-biodegradable polymers. It should be noted that Asian technology companies with more than five years of scientific and practical experience in the field of electronics processes have a variety of potential nanotechnology products that can be applied to a variety of nanofiber products for use in the medical and industrial fields. Isolation and filtration systems are noted.
Electrified nanofibers have a much longer length compared to the one-dimensional nanostructures obtained by other physical and chemical methods. Since electrification is a continuous process, the fiber length can be extended up to several kilometers. In the electrospinning process, these long fibers can be stacked in three dimensions to form porous woven or nonwoven membranes. In addition, the fibers produced are of very small diameter and surface to volume ratio. It should be noted that hollow nanofibers have a larger surface area to volume ratio than conventional solid nanofibers. This property is very important in chemical reactions, especially in catalytic and photocatalytic reactions.








Your comment submitted.